A Timer is Running on a 400 Khz Clock What Delay in Seconds Does the Continuous Mode
Contents
- 1 Basics
- 2 Timer 0 Basics
- 3 Timer 0 Example
- 3.1 Code
- 4 Timer 1 Basics
- 5 Timer 1 Example
- 5.1 Code
- 6 Timer 2
- 7 Downloads
Basics
Timers come in handy when you want to set some time interval like your alarm. This can be very precise to a few microseconds.

Timers/Counters are essential part of any modern MCU. Remember it is the same hardware unit inside the MCU that is used either as Timers or Counter. Timers/counters are an independent unit inside a micro-controller. They basically run independently of what task CPU is performing. Hence they come in very handy, and are primarily used for the following:
- Internal Timer: As an internal timer the unit, ticks on the oscillator frequency. The oscillator frequency can be directly feed to the timer or it can be pre-scaled. In this mode it used generate precise delays. Or as precise time counting machine.
- External Counter: In this mode the unit is used to count events on a specific external pin on a MCU.
- Pulse width Modulation(PWM) Generator: PWM is used in speed control of motors and various other applications.
Atmega32 has 3 timer units, timer 0, timer 1 and timer 2 respectively. Let us start our exploration with timer 0.
Timer 0 Basics
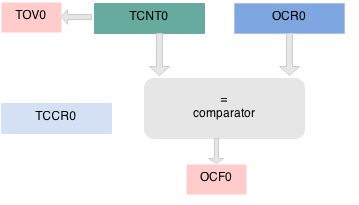
 Timer 0 is a 8 bit timer. It basically means it can count from 0 to 2^8 255. The operation of timer 0 is straight forward. The TCNT0 register hold the timer Count and it is incremented on every timer "tick". If the timer is turned on it ticks from 0 to 255 and overflows. If it does so, a Timer OverFlow Flag(TOV) is set.
Timer 0 is a 8 bit timer. It basically means it can count from 0 to 2^8 255. The operation of timer 0 is straight forward. The TCNT0 register hold the timer Count and it is incremented on every timer "tick". If the timer is turned on it ticks from 0 to 255 and overflows. If it does so, a Timer OverFlow Flag(TOV) is set.
You can as well load a count value in TCNT0 and start the timer from a specific count. Another interesting feature is that a value can be set in the Output Compare Register (OCR0), and whenever TCNT0 reaches that value, the Output Compare Flag (OCF0) flag is Set.
| TCNT0 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
The configuration of the Timer can be set using the TCCR0 register shown below. With this you can basically select two things:
- The Frequency of the Clock Source with CS02, CS01, CS00 bits.
- The mode of the timer. For the first example we will use it in normal mode where it ticks from zero to the highest value(255)
| TCCR0 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| FOC0 | WGM00 | COM01 | COM00 | WGM01 | CS02 | CS01 | CS00 |
| D2 | D1 | D0 | Clock Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| CS02 | CS01 | CS00 | Freq |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | No Clock (Stopped) |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | Clk |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | Clk/8 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | Clk/64 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | Clk/256 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | Clk/1024 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | Clk/T0-Falling edge |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | Clk/T0-Rising Edge |
| D6 | D3 | PWM |
|---|---|---|
| WGM00 | WGM01 | Mode |
| 0 | 0 | Normal |
| 0 | 1 | CTC (Clear timer on compare match) |
| 1 | 0 | PWM (Phase correct) |
| 1 | 1 | Fast PWM |
The Timer/counter Interrupt Flag Register(TIFR) holds the two basic flags we need the TOV and OVF. Other bits correspond to the timer interrupts, which we will look at in another tutorial.
| TIFR | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| OCF2 | TOV2 | ICF1 | OCF1A | OCF1B | TOV1 | OCF0 | TOV0 |
Timer 0 Example
Toggle LED connected to PD4 every 100msec using Timer Zero with 1024 pre-scalar in normal mode.
What is the Max delay Timer 0 overflow generates? Okay, lets calculate. The Explore Ultra AVR dev board comes with a 16MHz on board crystal and the fuse bits are set appropriately. If we use the highest pre-scalar of 1024, calculation shows it can generate a delay of 16milli seconds every time timer zero overflows.
$$Ftimer = CPU Frequency/Prescalar $$ $$Ftimer = 16MHz/1024 = 15.625KHz $$ $$Ttick = 1/ 15.625K = 64 \mu seconds$$ $$Ttotal = 64\mu s X 255 = 16ms$$
Of-course 16ms is not enough, so the next obvious question is:
How many times should the timer overflow to generate a delay of approximately 100msec?
$$ OverFlowCount = 100ms/16ms = 6.25 ≈ 6 $$
Now let's write a simple program which will toggle a port pin (PD4) after the timer 0 overflows 6 times.
- Load TCNT0 with 0x00
- Set CS00 and CS02 bits in TCCR0 register. This will start the timeWe will calculate the tick time in just a moment.r at Clk/1024 speed.
- Monitor the TOV0 flag in the TIFR0 register to check if the timer has over-flowed, keep a timerOverFlowCount.
- If timerOverFlowCount >= 6, toggle the led on PD4 and reset the count
Code
Timer 1 Basics
The Timer 1 is 16 bit, that means it can count from 0 to $$2^{16} = 65536$$. Hence the Timer/Counter 1 is a 16 bit registered formed out of TCNT1H and TCNT1L as shown below.
| TCNT1H | TCNT1L | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 | D10 | D9 | D8 | D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
Timer 3 also has 2 control registers which allow us to configure it and use it in any mode you wish.
| TCCR1A | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| COM1A1 | COM1A0 | COM1B1 | COM1B0 | FOC1A | FOC1B | WGM11 | WGM10 |
| TCCR1B | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| ICNC1 | ICES1 | - | WGM13 | WGM12 | CS12 | CS11 | CS10 |
| D2 | D1 | D0 | Clock Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| CS12 | CS11 | CS10 | Freq |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | No Clock (Stopped) |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | Clk |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | Clk/8 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | Clk/64 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | Clk/256 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | Clk/1024 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | Clk/T1-Falling edge |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | Clk/T1-Rising Edge |
Yes, and indeed we have a Flag register which will tell us the status of Timer 1 as shown below.
| TIFR | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| OCF2 | TOV2 | ICF1 | OCF1A | OCF1B | TOV1 | OCF0 | TOV0 |
Timer 1 Example
Let us repeat the example of Timer 0 of toggling PD4 every 100ms. This time since it is a 16 bit timer, let's see what is the max delay it generates with a pre-scalar of 1024.
$$Ftimer = CPU Frequency/Prescalar $$ $$Ftimer = 16MHz/1024 = 15.625KHz $$ $$Ttick = 1/ 15.625K = 64 \mu seconds$$ $$Ttotal = 64\mu s X 65536 = 4 seconds$$
So that is 4 secs! We just need 100 msec so, $$100ms/64\mu s = 1562 = 0x061A$$
This time, instead of using the overflow flag, it's use Output Compare Register (OCR) and the related flag.
So the with the following steps we should be able to generate the required delay.
- Load OCR1H with 0x3d and OCR1L with 0x09
- Run the timer with pre-scalar of 1024 by setting CS12 and CS10 bits.
- Monitor OCF flag and if it is set, toggle the led
- Reset the TCNT1L and TCNT1H values to zero and repeat steps 1 to 3.
Code
Timer 2
Well, timer 2 is pretty similar to the timers covered above. Give it a shot, should you've any questions do comment below.
Timers are independent units from the CPU. Hence if we use timers with Interrupts it can make the CPU free from polling the flags every-time. This is the way they are used normally. Check AVR Timer Interrupts tutorial where we will cover all of that.
Downloads
Download the complete project folder from the below link: https://github.com/ExploreEmbedded/ATmega32_ExploreUltraAvrDevKit/archive/master.zip
Have a opinion, suggestion , question or feedback about the article let it out here!
armstrongineclovent.blogspot.com
Source: https://exploreembedded.com/wiki/AVR_Timer_programming
0 Response to "A Timer is Running on a 400 Khz Clock What Delay in Seconds Does the Continuous Mode"
Post a Comment